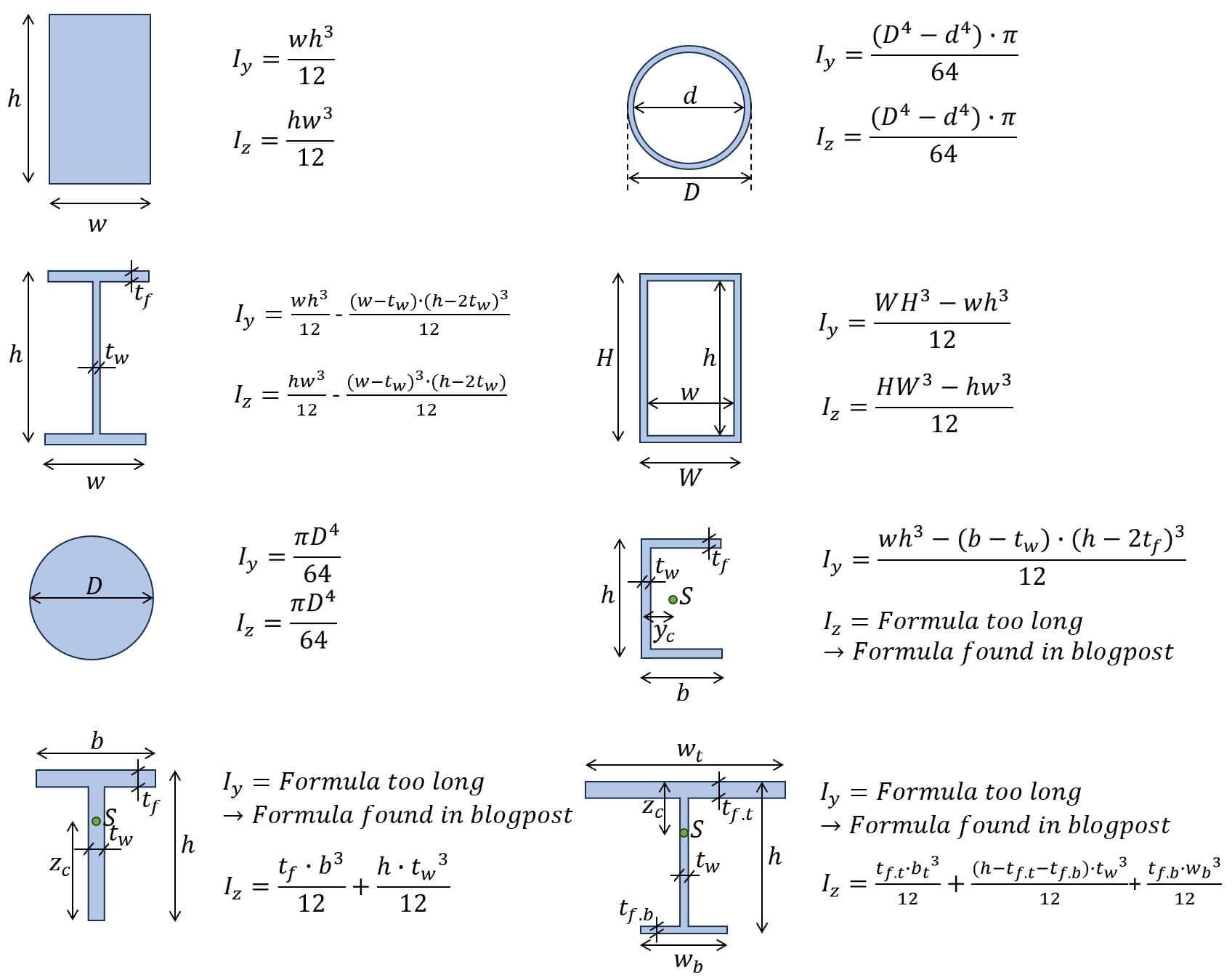
Moment Of Inertia Formulas For Different Shapes Structural Basics
The area moment of inertia (also called the second moment of area) defines the resistance of a cross-section to bending, due to the shape of the cross-sectio.

Moment of Inertia Using Mohr's Circle YouTube
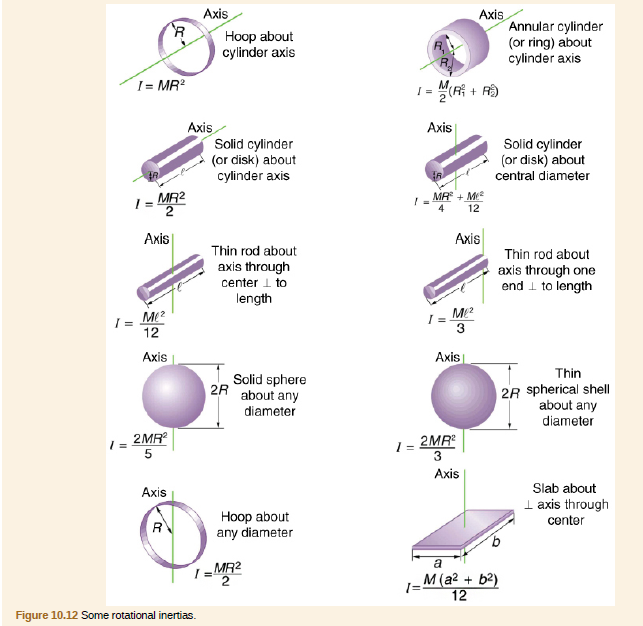
5.3 Newton's Second Law; 5.4 Mass and Weight; 5.5 Newton's Third Law; 5.6 Common Forces; 5.7. We want a thin rod so that we can assume the cross-sectional area of the rod is small and the rod can be thought of as a string of masses along a one-dimensional straight line.. We would expect the moment of inertia to be smaller about an axis.

Outstanding Moment Of Inertia Cheat Sheet Wave Optics Formula
Moment of Inertia calculators. Here is a list of the available calculation tools relative to the moment of inertia of a shape. More accurately, these tools calculate the second moment of area, which is a purely geometric property of a planar shape (not related to its mass). The second moment of area is commonly used in engineering disciplines.

Moment Of Inertia Second Moment Of Area Lecture2 Civil Stuff YouTube
Area moment of inertia, also known as second area moment or 2 nd moment of area, is a property of a two-dimensional plane shape, where it shows how its points are dispersed in an arbitrary axis in the cross-sectional plane. This property basically characterises the deflection of the plane shape under some load. Area moment of inertia is usually denoted by the letter I for an axis in a plane.

Statics Second Moment of Areas 3 YouTube
The area moment of inertia, also known as the second moment of area, is a property of a shape that measures its resistance to bending or deformation. It plays a significant role in structural engineering, especially in analyzing beams subjected to bending moments. The area moment of inertia depends on the shape and distribution of material.

Solved Statics Beam S Second Moment Inertia Also Known Ar
The area moment of inertia is a property of a two-dimensional plane shape which characterizes its deflection under loading. It is also known as the second moment of area or second moment of inertia. The area moment of inertia has dimensions of length to the fourth power. Unfortunately, in engineering contexts, the area moment of inertia is often called simply "the" moment of inertia even.
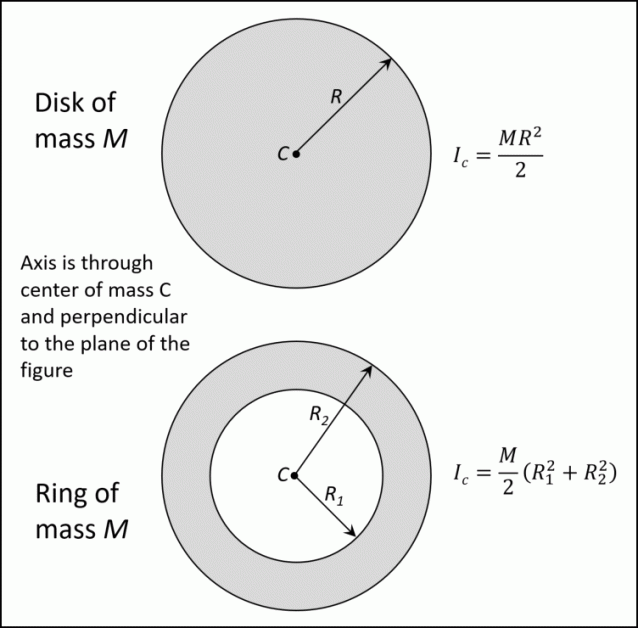
Moment of Inertia vs. Mass PocketLab
We can sum up the resistances to bending then by using the second rectangular area moment of inertia, where our distances are measured from the neutral axis. I = ∫A(dA ∗d2) (17.5.1) (17.5.1) I = ∫ A ( d A ∗ d 2) Assuming we put the origin point at the centroid and that the x x -axis is the neutral surface, the distance from the neutral.
Area Moment Of Inertia Cylinder Equation Tessshebaylo
The area moment of inertia, also called the second moment of area, is a parameter that defines how much resistance a shape (like the cross-section of a beam), has to bending because of its geometry. Consider a thin plank that supports a 100 kg load. The plank will be much less stiff when the load is placed on the longer edge of the cross-section.

Moment of inertia of a circle equation pnablack
The second moment of area (moment of inertia) is meaningful only when an axis of rotation is defined. Often though, one may use the term "moment of inertia of circle", missing to specify an axis. In such cases, an axis passing through the centroid of the shape is probably implied.

Engineering Mechanics Statics Theory Moment of Inertia Body) YouTube
The second moment of area is a geometric property. If we change the material type or grade, the second moment of area DOES NOT change. As we've already mentioned, the second moment of area has dimensions of length to the fourth power, L 4 L^4 L 4. 3.0 Geometric Axes and Sign Conventions

Parallel Axis Theorem for Area Moment of Inertia EngineerExcel
Mar 10, 2014 at 13:45. The linked post explains the interpretation of moment of inertia as a second moment of ρ ρ, from which a reinterpretation in the context of the second moment of area is pretty clear. 2nd moment of area equaling moment of inertia is technically incorrect in general, but it is correct (up to a constant factor) whenever ρ.
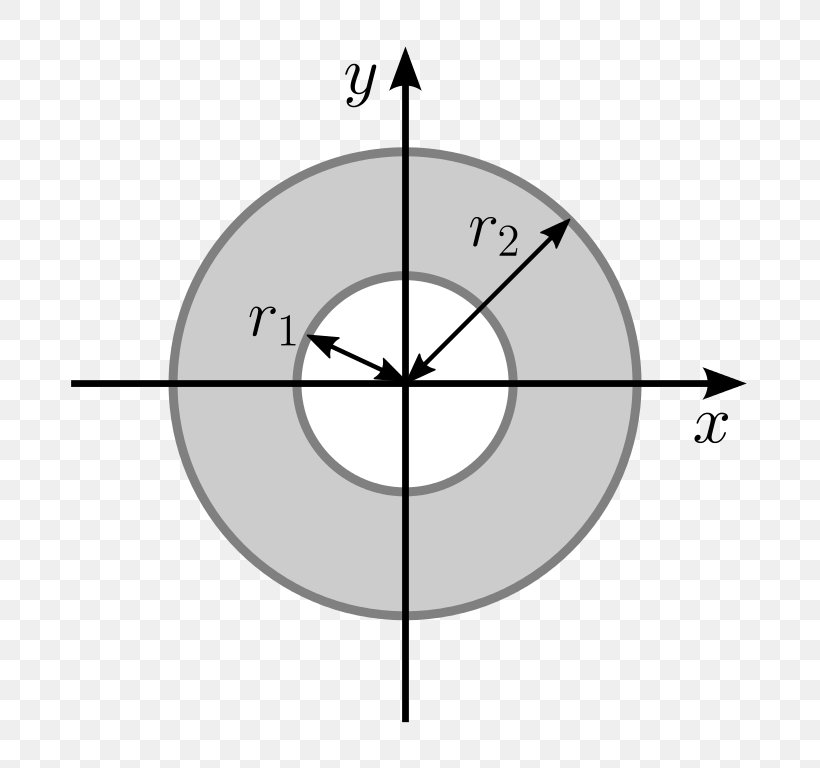
Circle Second Moment Of Area Moment Of Inertia First Moment Of Area, PNG, 768x768px, Second
Polar Area Moments of Inertia. Rectangle. Area = bh A r e a = b h. Ix Iy = 1 12bh3 = 1 12b3h I x = 1 12 b h 3 I y = 1 12 b 3 h. Jz = 1 12bh(b2 +h2) J z = 1 12 b h ( b 2 + h 2) Right Triangle. Area = 1 2bh A r e a = 1 2 b h. Ix Iy = 1 36bh3 = 1 36b3h I x = 1 36 b h 3 I y = 1 36 b 3 h. Ix.
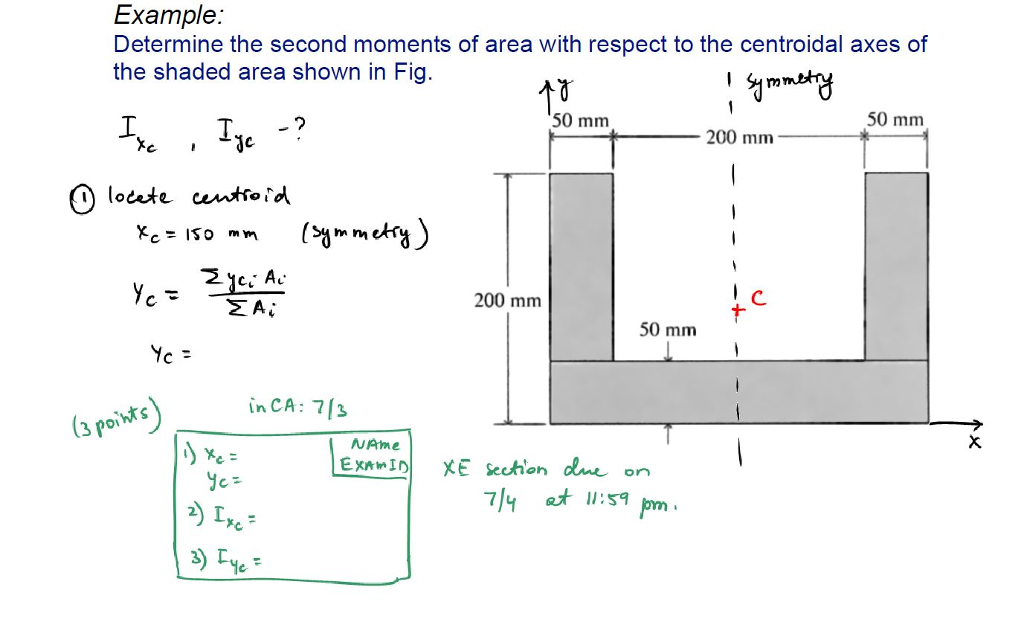
Solved Determine the second moments of area with respect to
The second polar moment of area, also known (incorrectly, colloquially) as "polar moment of inertia" or even "moment of inertia", is a quantity used to describe resistance to torsional deformation (), in objects (or segments of an object) with an invariant cross-section and no significant warping or out-of-plane deformation. It is a constituent of the second moment of area, linked through the.

Second Moment Of Area Cylinder Equation Diy Projects
The moment of inertia can be derived as getting the moment of inertia of the parts and applying the transfer formula: I = I 0 + Ad 2. We have a comprehensive article explaining the approach to solving the moment of inertia. Fundamentally, the moment of inertia is the second moment of area, which can be expressed as the following:
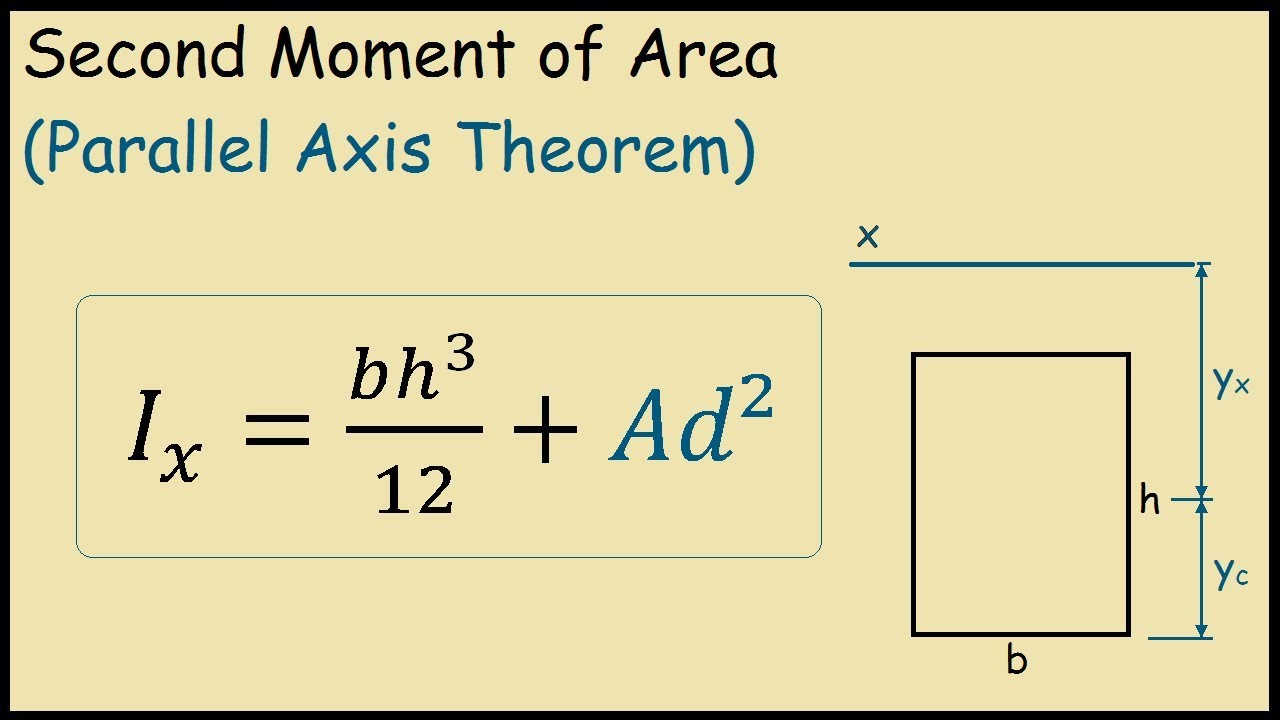
Second Moment of Area of a Rectangle (Parallel Axis Theorem) YouTube
Area Moment of Inertia or Moment of Inertia for an Area - also known as Second Moment of Area - I, is a property of shape that is used to predict deflection, bending and stress in beams.. Area Moment of Inertia - Imperial units. inches 4; Area Moment of Inertia - Metric units. mm 4; cm 4; m 4; Converting between Units. 1 cm 4 = 10-8 m 4 = 10 4 mm 4; 1 in 4 = 4.16x10 5 mm 4 = 41.6 cm 4.

Torsional Stress Torsion Formula Derivation & Polar Second Moment of Area (Polar Moment of
In this video we introduce the second moment of area / inertia and its significance in the behaviour of a structure, learning how to determine the second mom.
- Geloof Hoop En Liefde Quotes
- Land In Afrika 4 Letters
- Toyota Corolla Quest South Africa
- Foto Laten Zien Bij Bellen Iphone
- Nintendo Switch Oled Met Spel
- Formule 1 Hotels Frankrijk Kaart
- Ste Marie De La Mer
- Mary Oliver The Wild Geese
- Gebouwen Voor Reizende Handelaren En Marktplaats
- Mag De Politie Je Auto Doorzoeken
