
The Difference Between Layer 2 And Layer 3 Industrial Switches?
Layer 2 Switch vs. Layer 3 Switch. Layer 2 switch is used to switch data. This switch uses the MAC address operating system. Network traffic can be managed effectively using this switch. Its broadcast domain is single. Layer 3 switch is used to switch and route data. This switch uses an IP address as an operating system.

Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Netwerk Switches
A Layer 2 managed switch is designed to forward traffic between network hosts within the same subnet, based on the entries in its MAC address table. On the other hand, a Layer 3 managed switch is capable of forwarding traffic between different subnets, using a map of the IP network maintained in its routing table.
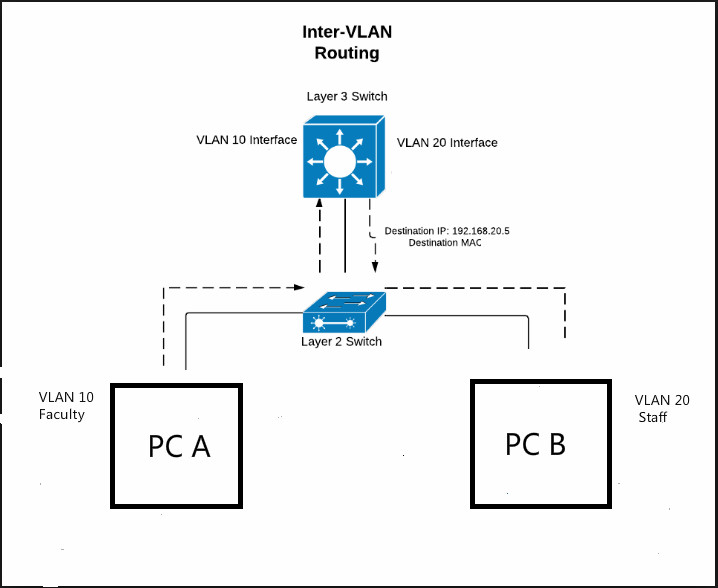
Inter VLAN Routing Layer 3 Switch vs Router
The main thing to remember when comparing layer 2 vs layer 3 switches is that the difference is in the routing capability of the switch. With layer 2 switches, there is no routing algorithm used and instead, the switch uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to switch data from a physical port to a MAC address and compiles a MAC table for future.

Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switches YouTube
A layer 2 switch can only switch packets from one port to another, whereas a layer 3 switch can both switch and route. Routing is not possible in Layer 2 switching, which means that devices can communicate within the same network. In Layer 3 switching, devices can communicate inside and outside the network. MAC and IP address.
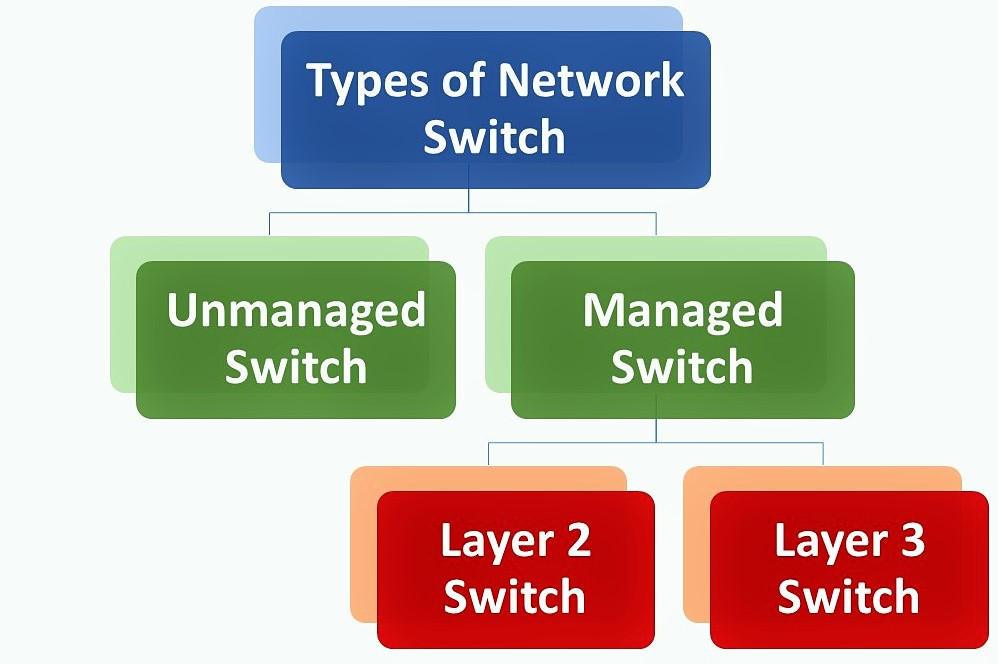
Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches in Networking My Computer Notes
Choosing between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches means weighing simple use against the need for deep network control and growth potential. For small setups, Layer 2 devices offer ease without added complexity, proving both efficient and cost-saving. Yet, when a network's requirements grow, Layer 3 units stand out.

Layer 2 Vs Layer 3 Switch, What's the Difference? VSOL
Layer 2 vs Layer 3. When it comes to network switches, you have a lot of options. Finding the perfect switch for every occasion can be a monstrous task. Sometimes, the easiest way to find a good choice is to take a step back and learn more about the primary differences that exist between switches.
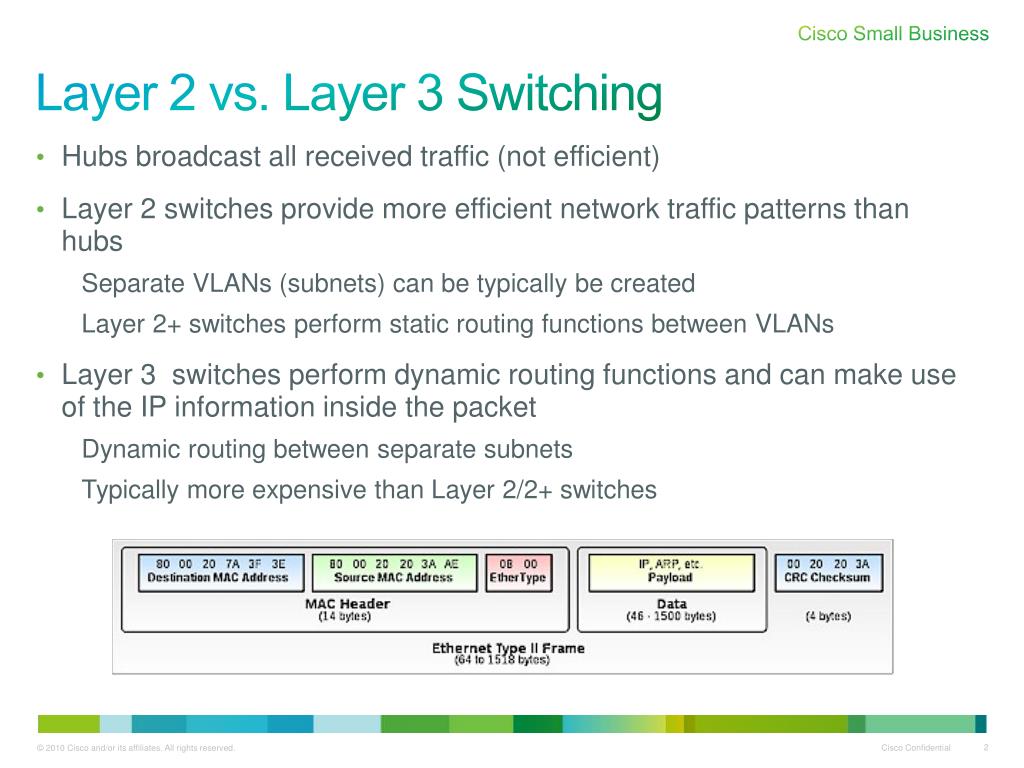
PPT Switching 101 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6147659
This blog explains about Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching, including the OSI networking model, Ethernet protocols, and the role of routers and switches in network segmentation. Dive into the benefits and applications of both Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches, and discover how to choose the right one for your network's size, complexity, and traffic patterns.

Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 Switches Technology USA
The main difference between a Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch is the routing function. A Layer 3 switch (also called a multilayer switch) performs all the functions a Layer 2 switch does; however, it has both static and dynamic routing functions. In other words, Layer 3 switching combines the functionality of both a switch and a router by inspecting.

Layer 3 vs Layer 3 Lite vs Layer 2+ Switches YouTube
The differences between layer 2, 3 and 4 networking switches as well as their benefits and shortfalls. What to consider when looking at your next switch in relation to your individual network. Layer 2 Networking Switch. Layer 2 networking switches sit within layer 2 of the TCP/IP model for networking, also known as the data link layer.

Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Network Switch A Guide To Choosing The Right One For Your Business Tech Zarar
Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches are essential components of modern computer networks. They play a crucial role in facilitating communication between devices and ensuring efficient data transmission. However, understanding the differences between these two types of switches is vital when it comes to choosing the right option for your network.

Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 Network Switches What's the Difference? CEPRO
Layer 2 switches offer high-speed connectivity, while Layer 3 switches provide routing, QoS, and security. For example, Layer 2 buttons can be used for device connectivity in an organization with multiple VLANs, while Layer 3 switches handle routing and advanced networking services.

Layer 2 vs layer 3 switch CompTIA Network+ N10008 Domain 2.2 YouTube
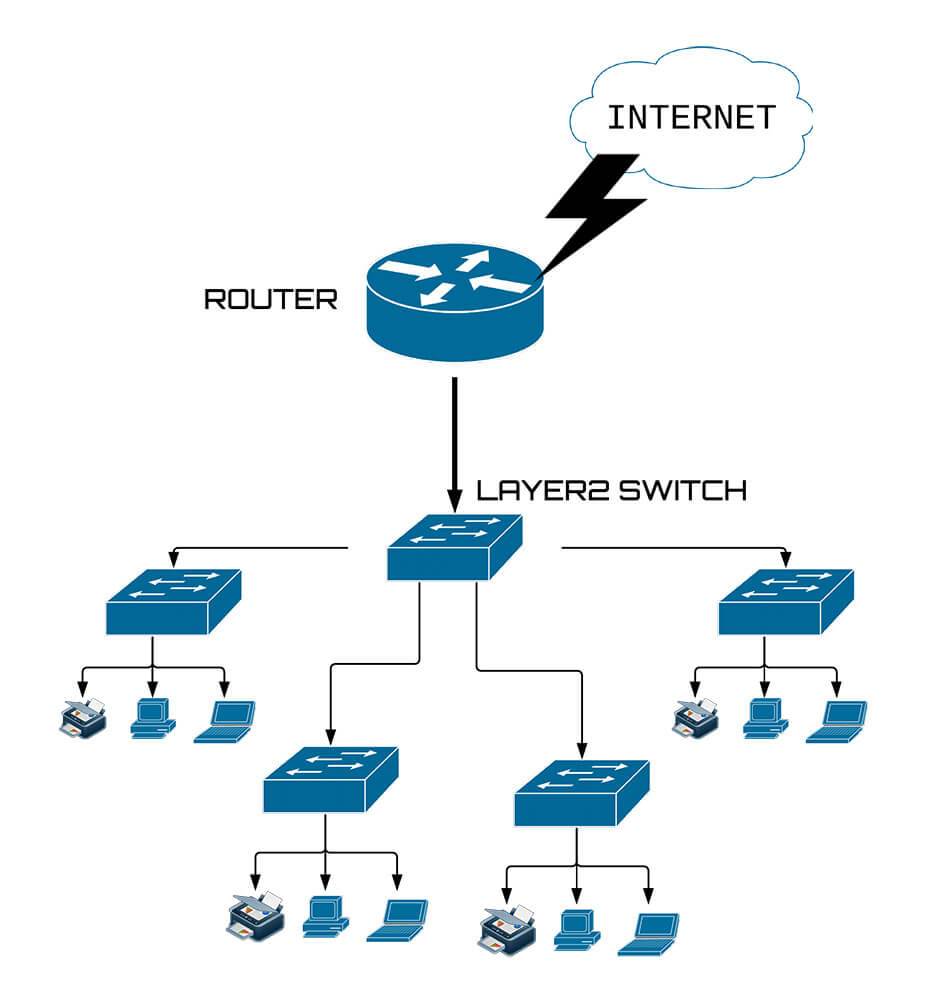
Layer 2 switch work on layer 2 of OSI model i.e. data link layer and sends a "Frames" to destination port using MAC address table which stores the mac address of a device associated with that port. Layer 3 switch work on layer 3 of OSI model i.e. network layer where it route packet by using IP address, it is used widely on VLANs. Layer 2.

Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switch Which One Do You Need?,English
The difference between a Layer 2 switch and a Layer 3 switch is absolute. At Layer 3, Layer 2 switches cannot route packets. In contrast to Layer 2 switches, Layer 3 employs IP addresses for routing. It is a specialized piece of hardware that routes packets. Switches at the Layer 3 layer can switch quickly and have more ports.
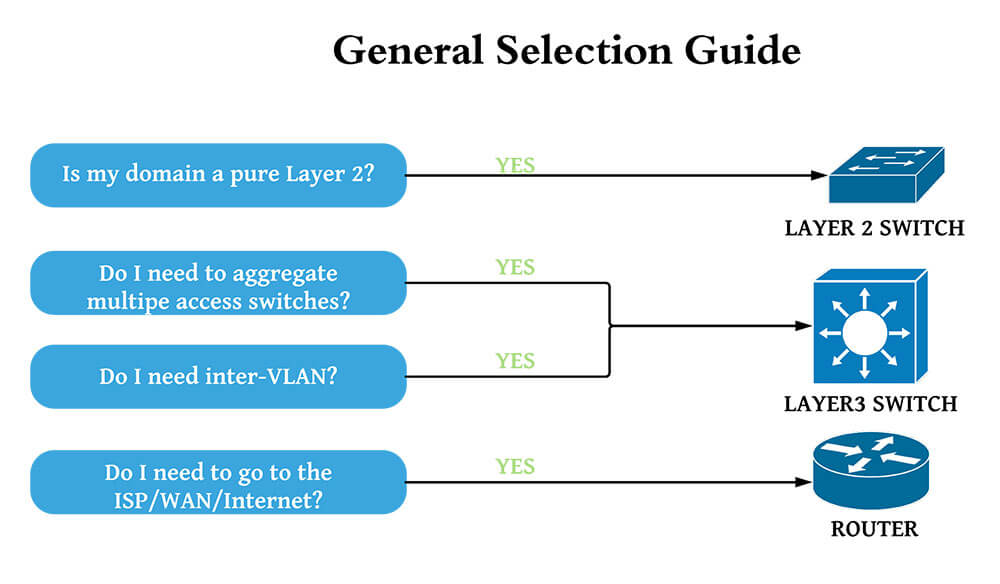
Basic facts about Layer 2 & Layer 3 Switches Learn what the differe
Layer 2 switches are used to reduce traffic on the local network, whereas Layer 3 switches mostly used to Implement VLAN. The advantage of Layer 2 switches is that it helps to forward packets based on unique MAC addresses. The advantage of Layer 3 switches offers flow accounting and high-speed scalability.
Basic facts about Layer 2 & Layer 3 Switches Learn what the differe
The layer 3 vs 2 refers to the OSI model. A layer 3 switch supports routing. A layer 2 switch only knows ethernet, you may be able to setup VLANs. Share. Improve this answer. answered Mar 18, 2010 at 6:29. Zoredache. 132k 41 281 422. Adding to that a layer 2 switch normally does hardware routing.
Basic facts about Layer 2 & Layer 3 Switches Learn what the differe
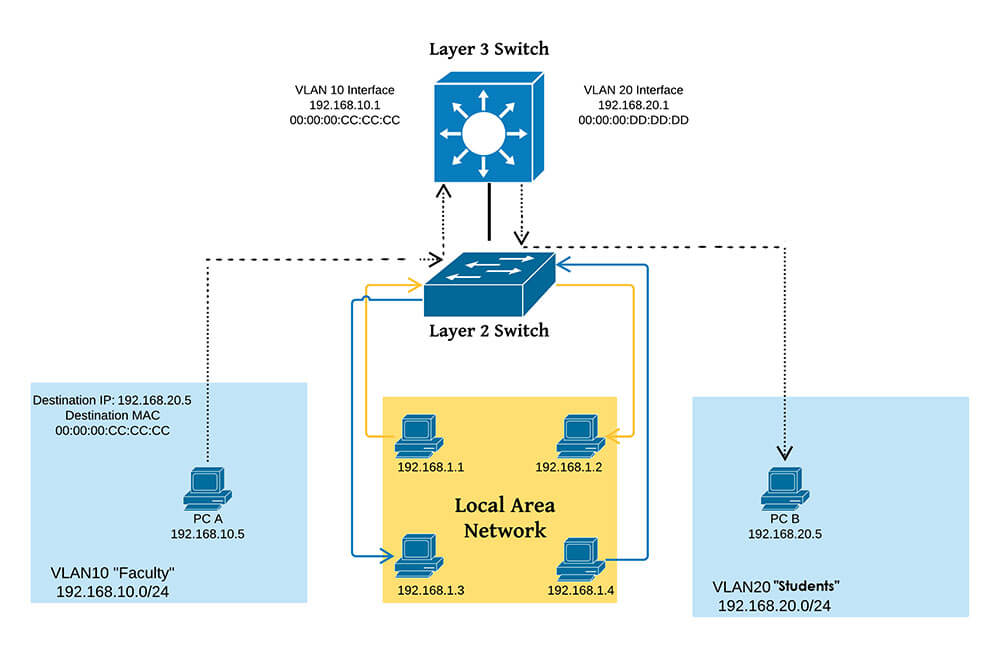
Layer 2 (MAC) vs Layer 3 (IP) Network Switches. The main function of a Layer 2 is to help the traffic from devices within a LAN reach each other. A Layer 2 switch does this by keeping a table of all the MAC addresses it has learned and what physical port they can be found on. The MAC address is something that operates within Layer 2 of the OSI.
- Mclaren F1 Remote Control Car
- Corry Konings Adio Adio Adio
- La Sociedad De La Nieve Waargebeurd Verhaal
- P I Alphen Aan De Rijn
- Zadig E Voltaire Just Rock
- Cf Compact Flash Card Reader
- Hoe Lang Duurt Een Master
- How Much Does A Coffee Bean Weigh
- Jamie Oliver S Diner Piccadilly London
- Zoe Overleden Nesselande 17 Juni 2023
