Free picture characteristics, streptococcus pneumoniae, bacteria, colonies
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococci) are gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic, aerobic, encapsulated diplococci. Pneumococcal infection is a major cause of otitis media, pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis, and death. Diagnosis is by Gram stain and culture. Treatment depends on the resistance profile and includes either a beta-lactam, a macrolide, a.
Streptococcus Pneumoniae Bacteria Culture 1 Photograph by Daniela Beckmann Fine Art America
Healthcare providers test for Streptococcus pneumoniae to diagnose pneumococcal disease and rule out other conditions. Your healthcare provider does a physical exam and asks you about your medical history and current symptoms. Your provider may use tests such as: Blood test (complete blood count or CBC). Urine test . Phlegm test. Chest X-ray.
_on_Columbia_Horse_Blood_Agar.jpg)
FileStreptococcus pyogenes (Lancefield Group A) on Columbia Horse Blood Agar.jpg Wikimedia
Fig 14.2.6 14.2. 6: A Plate of Blood Agar Showing Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Hemolysis (Indirect Lighting) Fig. 14.2.7 14.2. 7: A Blood Agar Plate of a Throat Culture Showing Possible Streptococcus pyogenes. Alpha-, beta-, and gamma-hemolytic bacteria were streaked to form of the Greek letters alpha, beta, and gamma.

Pathology Outlines Klebsiella oxytoca
On blood agar plates some of the strains give an wide-zone alpha hemolytic reaction after extended incubation. Identifying these bacteria is difficult and an extended set of physiologic characteristics may have to be determined before final identification is possible.. Streptococcus pneumoniae: S. pneumoniae cultures are α-hemolytic on.

streptococcuspneumoniae_pleurav_gram4_f Grace BioLabs
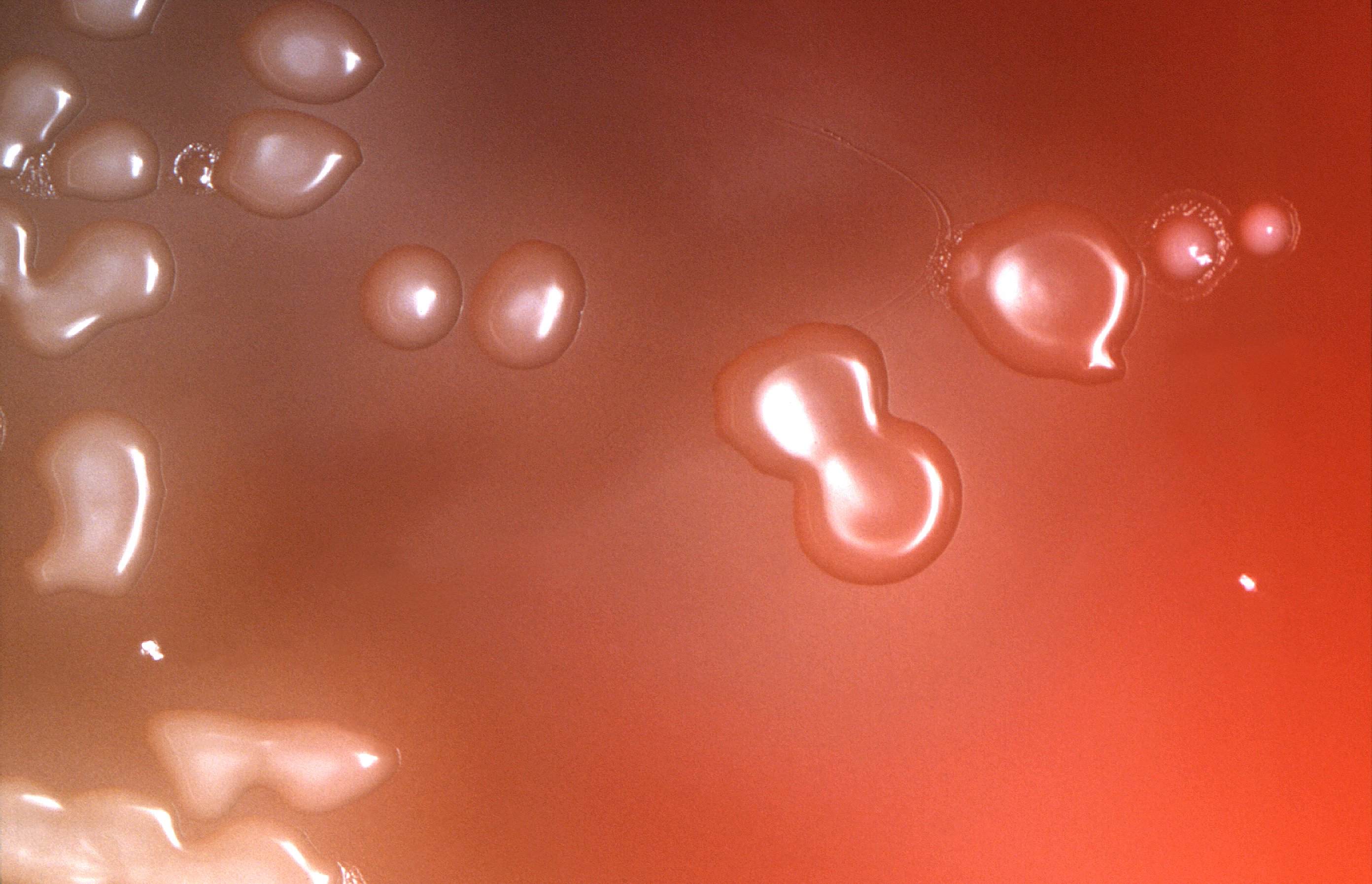
BIOL 230 Lab Manual: Streptococcus pneumoniae on Blood Agar. Note the mucoid colonies, alpha hemolysis (greenish discolorization of the red blood cells around the colonies) and sensitivity to the drug optochin in the Taxo P® disc. Photograph from From MicrobeLibrary.org. Courtesy of Rebecca Buxton, University of Utah.
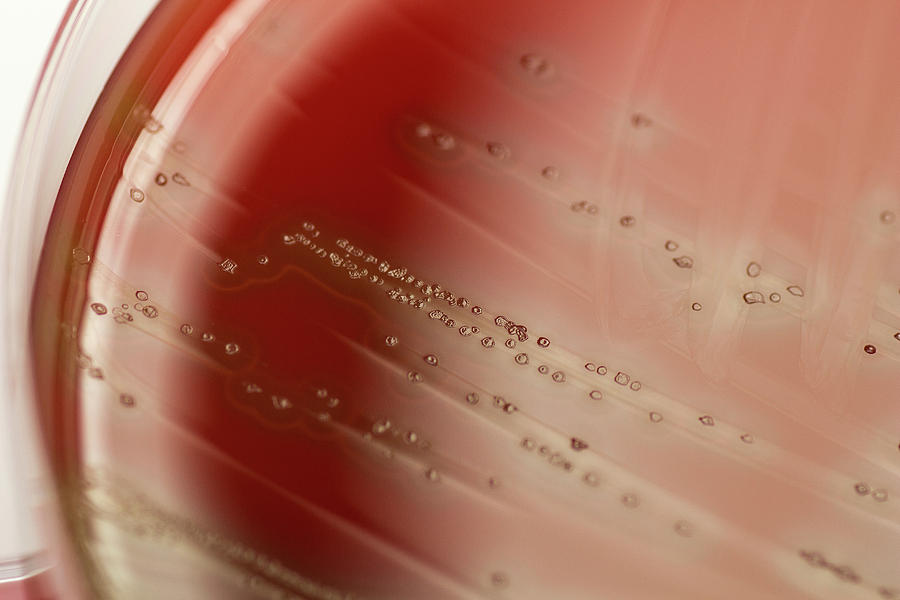
200+ Blood Agar Plates Stock Photos, Pictures & RoyaltyFree Images iStock
They found that selection on blood agar increased the number of differentially expressed genes from 113 genes after 50 passages to 706 genes (or approximately 1/3 of the pneumococcus genome) after 100 passages.. The effect of protein expression of Streptococcus pneumoniae by blood. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39, 703-708.

Streptococcus pneumoniae Microbiology, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Med lab
Streptococcus pneumoniae are lancet-shaped, gram-positive, facultative anaerobic bacteria with more than 100 known serotypes.Most S. pneumoniae serotypes can cause disease, but only a minority of serotypes produce the majority of pneumococcal infections.. Carriage of pneumococci. Pneumococci are common inhabitants of the respiratory tract. The bacteria may be isolated from the nasopharynx of 5.
Streptococcus pneumoniae antigen The Native Antigen Company
Species such as Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Streptococcus agalactiae are highly virulent and cause infections and diseases such as scarlet and rheumatic fevers,. and exhibit gamma-hemolysis on blood agar, although some strains are alpha-hemolytic or beta-hemolytic [14,15].

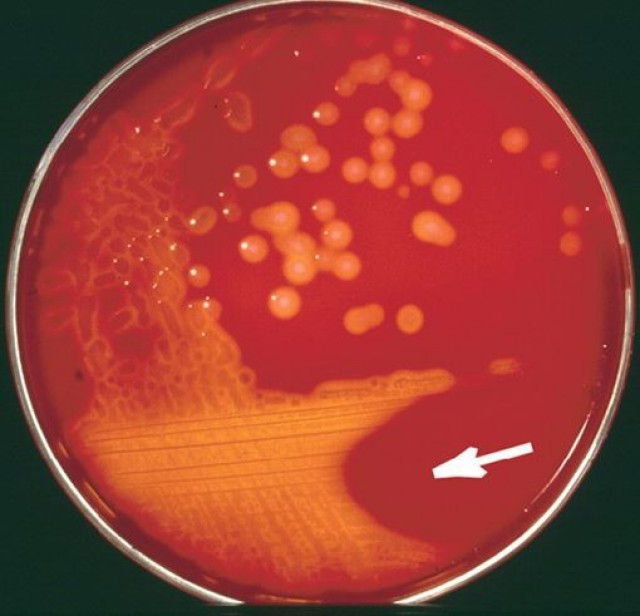
A virulent strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) growing on blood agar. Colonies
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a leading cause of bacterial pneumonia and is the principal cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide.. -containing blood-agar plates to select for the inactivated.
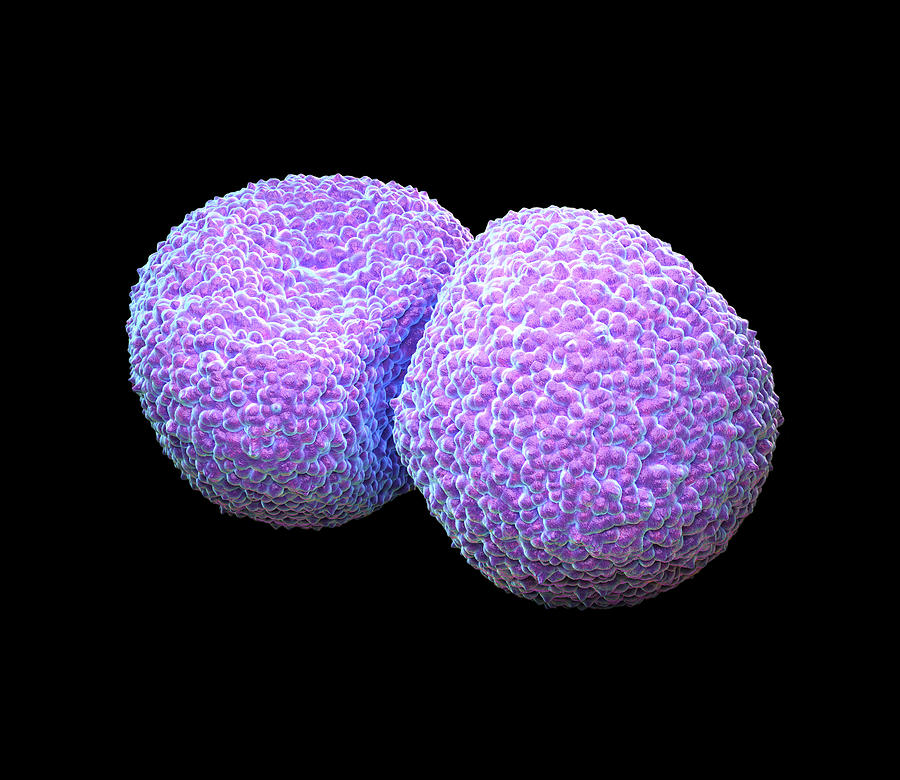
Streptococcus Pneumoniae Bacteria Photograph by Roger Harris
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram-positive, lancet-shaped bacterium and a cause of community-acquired pneumonia. Pneumococcal infections are present throughout the world and are most prevalent during the winter and early spring months.. Blood cultures are positive in only 20% to 25% of all pneumonia cases that are caused by S. pneumonia.

Figure9.15 Streptococcus pneumoniae on Blood Agar Download Scientific Diagram
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or the pneumococcus, is a gram-positive coccus usually appearing as a diplococcus, but occasionally appearing singularly or in short chains. Cocci are slightly pointed or "lancet-shaped". Encapsulated and non-motile. Catalase negative. Alpha-hemolytic (Figure 15.1.2.2.1.1 15.1.2.2.1.

Columbia Blood Agar with Sheep Blood Medium
Streptococcus pneumoniae and other streptococci produce a greenish halo on blood agar plates referred to as alpha-hemolysis. This phenotype is utilized by clinical microbiology laboratories to report culture findings of alpha-hemolytic streptococci, including S. pneumoniae, and other bacteria.The alpha-hemolysis halo on blood agar plates has been related to the hemolytic activity of.
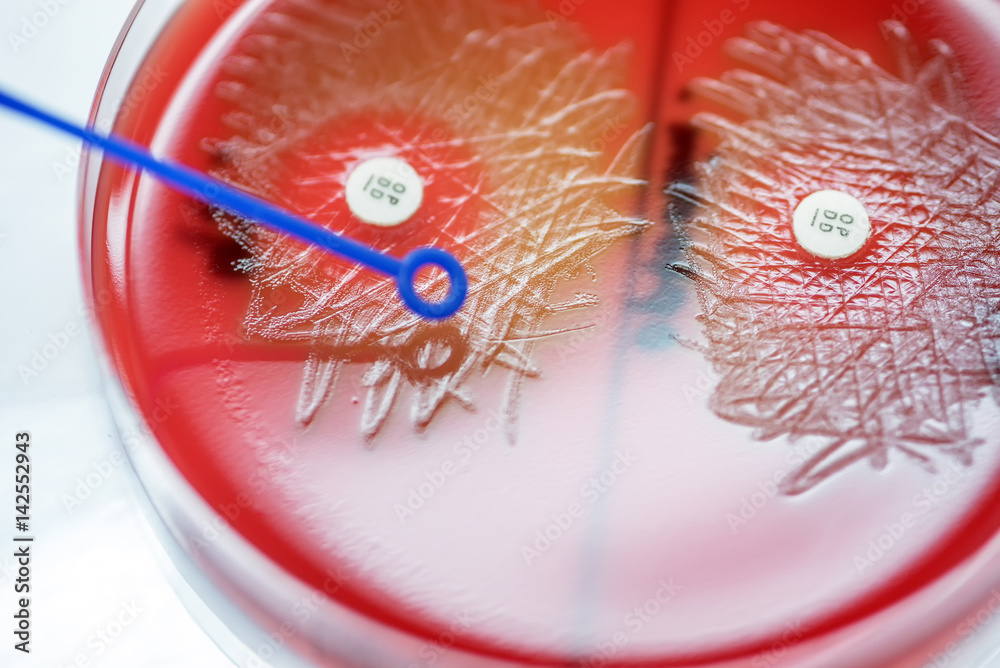
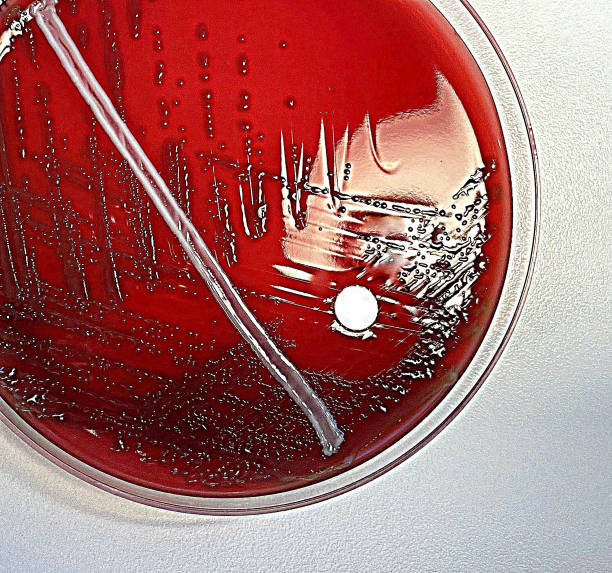
Optochin subsensitivity test on blood agar plate contains small light grains for Streptococcus
Despite the clinical importance and frequent isolation of Streptococcus pneumoniae, there is no one "gold standard" or reference method for its identification.Laboratory identification of this pathogen has been accomplished using one or more assays, including Gram stain morphology, colony morphology, and hemolysis on sheep blood agar, pyrrolidonyl arylamidase reactivity, optochin.

What Are the Symptoms of Streptococcus Pneumoniae?
MICROBIOLOGY DIAGNOSIS: Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria are gram-positive cocci arranged in chains and pairs (diplococci) on microscopic examination. A green, α-hemolytic, zone surrounds S. pneumoniae colonies on blood-agar plates. Pneumococci can be differentiated from other catalase-negative viridans streptococci by their susceptibility to Optochin and solubility in bile salts.

Anja Ubbink (Anja2heart) / Twitter
Scientific Reports - Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae by a real-time PCR assay targeting SP2020.. onto blood agar plates supplemented with 5 µg/mL gentamicin, and grown overnight in.
Streptococcus pyogenes, enemiga silenciosa
Streptococcus pneumoniae colonizes the mucosa of the upper respiratory tract (URT). This carriage is the prerequisite for both transmission to other individuals and invasive disease in the carrier.
- New Season Of My Hero Academia
- De Slimste Mens Eerste Aflevering
- Mka Kliniek Utrecht Mka Klinieken Nederland
- All You Need Is Love Kerstspecial Gemist
- Waar Is Fargo Te Zien
- Tekeningen Om In Te Kleuren
- 3 5 Mm To Bluetooth Converter
- Nederlanders In De Giro 2023
- Whos Afraid Of Red Yellow And Blue
- Naar Welke Club Gaat Ronaldo
